Classification
1、Immunocolloidal gold staining based on light microscope :Cell suspension smears or tissue sections can be stained by colloidal gold labeled antibodies; alternatively, silver developer can be adopted to enhance the marker based on colloidal gold labeling, so that the reduced silver atoms deposit on the surface of labeled gold particles; in this way, sensitivity of colloidal gold markers are significantly improved.
2、Immunocolloidal gold staining based on electron microscope:The colloidal gold labeled antibodies or antiantibodies may bind to negatively stained virus samples or ultrathin tissue sections; after that, negative staining is carried out. Moreover, such an approach can be performed to observe virus morphology and detect viruses.
3����、Dot-immunogold filtration assay:A millipore filter (e.g., membrane) is selected as the vector. Firstly, antigens or antibodies are dotted on the filter and then closed; secondly, the specimen to be detected is added; after washing, the colloidal gold labeled antibodies are used to detect corresponding antigens or antibodies.
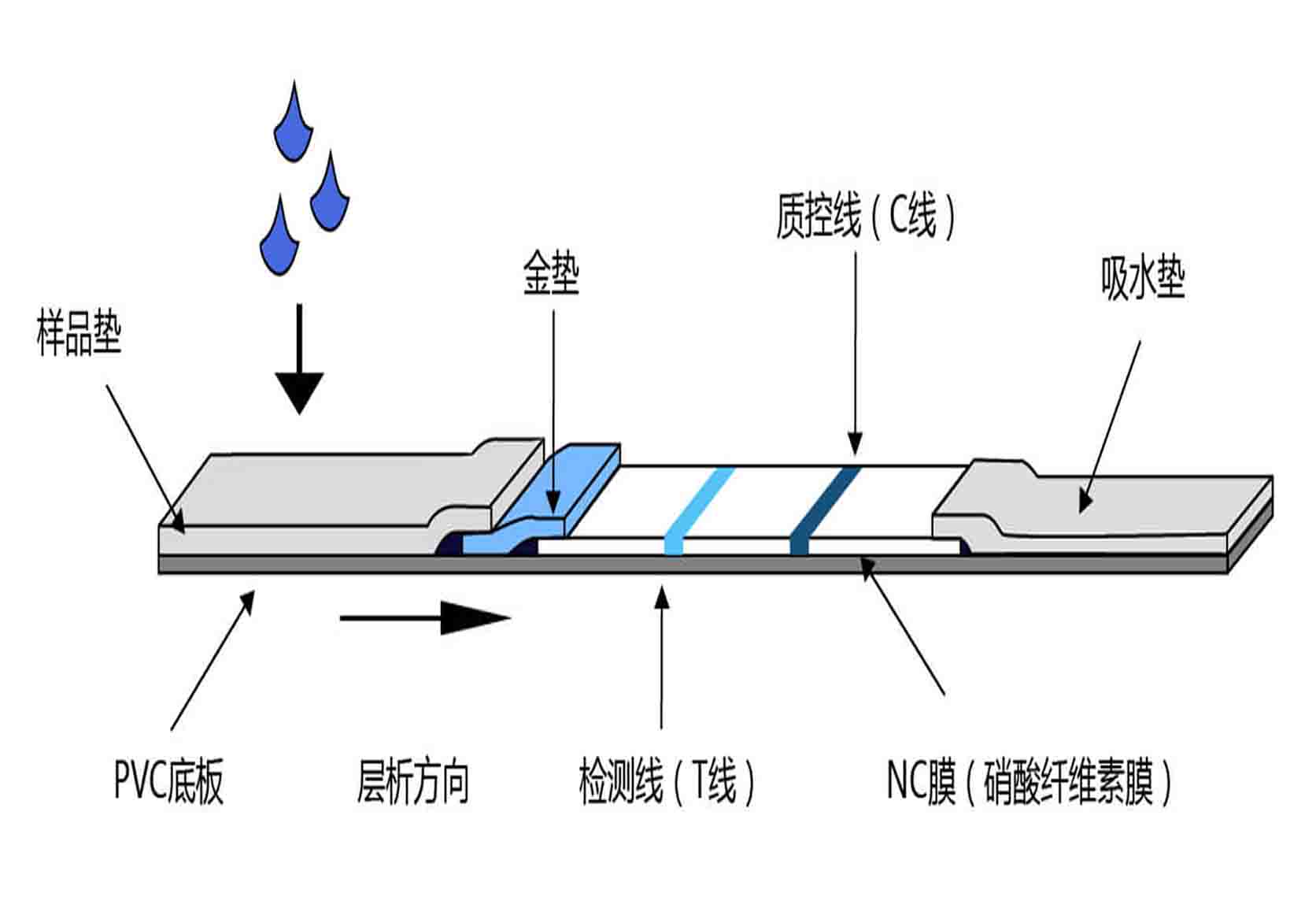
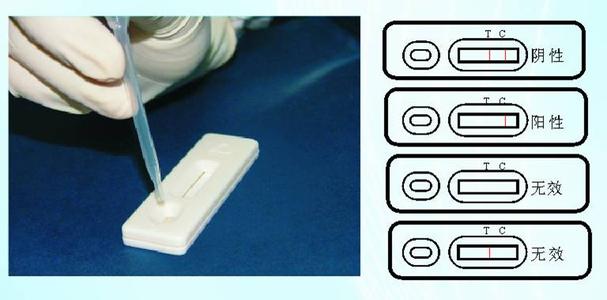
4、Colloidal gold immunochromatography:Specific antigens or antibodies in a stripped shape are fixed on the filter; and, colloidal gold labeling reagent (antibodies or monoclonal antibodies) are adsorbed on the conjugate pad. Once the test sample has been added on a sample pad at one end of the test strip, it moves forward under the capillary action, so that colloidal gold labeling reagent on the conjugate pad is dissolved and mutually react with it; subsequently, when it moves to an area of the fixed antigens or antibodies, it is entrapped because of specific binding that takes place between it and conjugates of the test substance and the colloidal gold reagent; as a result, the test sample is accumulated on the test strip and the corresponding staining outcome can be observed by naked eyes. Now, diagnostic strips of convenient use have been developed based on such a method.
5��、Rapid colloidal gold reagent detection method:Specific antibodies are firstly fixed on a zone of acid cellulose membrane. Once an end of the dry acid cellulose is immersed into the sample (urine or serum), the sample moves forward along the membrane due to a capillary action; when it moves to the zone where the antibodies are fixed, specific binding takes place between corresponding antigens in the sample and the antibodies. Meanwhile, considering a high electron density feature of gold particles, red dots become visible to naked eyes at a position where colloidal gold proteins bind to each other under the circumstance that these markers extensively accumulate at relevant ligands. This is the principle of rapid colloidal gold reagent detection method. The key to producing rapid and precise reagent lies in the fact whether sensitivity and specificity of raw materials such as monoclonal antibodies, polyclonal antibodies, antigens, haptens, chimeric substances of proteins, and colloidal gold meet the highest standards. This is the most important criterion for colloidal gold reagent reagent.